티스토리 뷰
Directory Structure
Logical directory structure
- Flat (single-level) directory structure
- 2-level directory structure
- Hierarchical (tree-structure) directory structure
- Acyclic graph directory structure
- General graph directory structure
Flat Directory Structure
- FS내에 하나의 directory만 존재
- Single-level directory structure
- Issues
- File naming
- File protection
- File management
- * 다중 사용자 환경에서 문제가 더욱 커짐

2-Level Directory Structure
- 사용자 마다 하나의 directory 배정
- 구조
- MFD (Master File Directory)
- UFD (User File Directory)
- Problems
- Sub-directory 생성 불가능
- File naming issue
- 사용자간 파일 공유 불가
- Sub-directory 생성 불가능

Hierarchical Directory Structure
- Tree 형태의 계층적 directory 사용 가능
- 사용자가 하부 directory 생성/관리 가능
- System call이 제공되어 야 함
- Terminologies
- Home directory, Current directory
- Absolute pathname, Relative pathname
- 대부분의 OS가 사용

Acyclic Graph Directory Structure
- Hierarchical directory structure 확장
- Directory안에 shared directory, shared file를 담을 수 있음
- Link의 개념 사용
- E.g., Unix system의 symbolic link


General Graph Directory Structure
- Acyclic Graph Directory Structure의 일반화
- Cycle을 허용
- Problems
- File 탐색 시, Infinite loop를 고려해야 함

File Protection
- File에 대한 부적절한 접근 방지
- 다중 사용자 시스템에서 더욱 필요
- 접근 제어가 필요한 연산들
- Read (R)
- Write (W)
- Execute (X)
- Append (A)
File Protection Mechanism
- 파일 보호 기법은 system size 및 응용 분야에 따라 다를 수 있음
- Password 기법
- 각 file들에 PW 부여
- 비현실적
- 사용자들이 파일 각각에 대한 PW를 기억해야 함
- 접근 권한 별로 서로 다른 PW를 부여 해야 함
- Access Matrix 기법
Access Matrix
- 범위(domain)와 개체(object)사이의 접근 권한을 명시
- Terminologies
- Object
- 접근 대상 (file, device 등 HW/SW objects)
- Domain (protection domain)
- 접근 권한의 집합
- 같은 권한을 가지는 그룹 (사용자, 프로세스)
- Access right
- <object-name, rights-set>
- Object
Example

- 각각의 파일(Object)에 대한 권한(Domain)을 명시한 Table
Implementation
- Global table
- Access list
- Capability list
- Lock-key mechanism
Global Table
- 시스템 전체 file들에 대한 권한을 Table로 유지
- <domain-name, object-name, right-set>

단점
- 빈 공간에 대해서도 저장이 필요 -> Large table size -> overhead
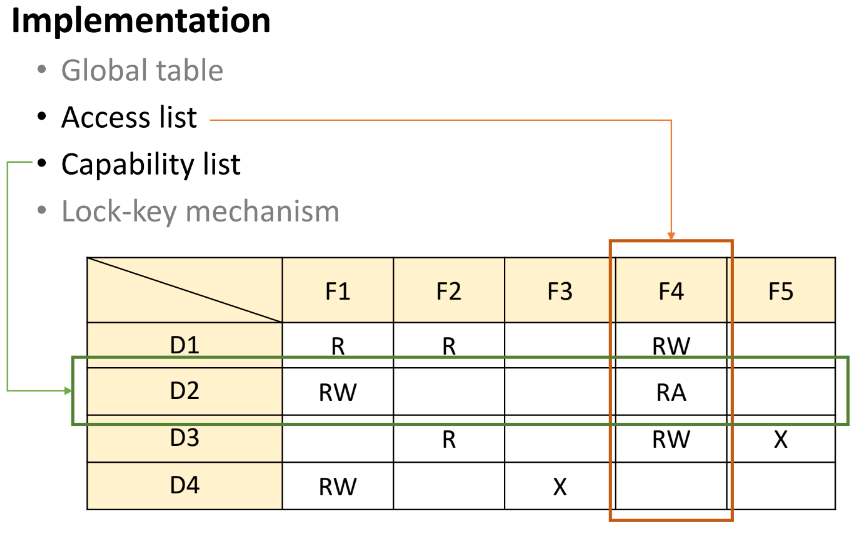
Access List
- Access matrix의 열(column)을 list로 표현
- 각 object에 대한 접근 권한을 나열
- Alist(Fk) = { <D1, R1>, <D2, R2>, ..., <Dm, Rm> }
- Object 생성 시, 각 domain에 대한 권한 부여
- Object 접근 시 권한을 검사
- 실제 OS에서 많이 사용됨
- UNIX의 예

- 파일에 접근 할 때마다 체크해야 한다 -> overhead
Capability List
- Access matrix의 행(row)을 list로 표현
- 각 domain에 대한 접근 권한 나열
- Clist(D1) = { <F1, R1>, <F2, R2>, ...., <Fp, Rp> }
- Capability를 가짐이 권한을 가짐을 의미
- 프로세스가 권한을 제시 , 시스템이 검증 승인
- 시스템이 capability list 자체를 보호 해야 함
- Kernel안에 저장
Lock-key Mechanism
- Access list와 Capability list를 혼합한 개념
- Object는 Lock을, Domain은 Key를 가짐
- Lock/key : unique bit patterns
- Domain 내 프로세스가 object에 접근 시,
- 자시의 key와 object의 lock 짝이 맞아야 함
- 시스템은 key list를 관리해야 함
Comparison of Implementations
- Global table
- Simple, but can be large
- Access list
- Object 별 권한 관리가 용이함
- 모든 접근 마다 권한을 검사해야 함
- Object 많이 접근하는 경우 → 느림
- Capability list
- List내 object들(localized Info.)에 대한 접근에 유리
- Object 별 권한 관리(권한 취소 등)가 어려움
- 많은 OS가 Access list와 Capability list 개념을 함께 사용
- Object에 대한 첫 접근 → access list 탐색
- 접근 허용 시, Capability 생성 후 해당 프로세스에게 전달
- 이후 접근 시에는 권한 검사 불필요
- 접근 허용 시, Capability 생성 후 해당 프로세스에게 전달
- 마지막 접근 후 → Capability 삭제
- Object에 대한 첫 접근 → access list 탐색
강의
www.youtube.com/watch?v=3VOqyi-wbJU&list=PLBrGAFAIyf5rby7QylRc6JxU5lzQ9c4tN&index=40
www.youtube.com/watch?v=zrzbETkxljM&list=PLBrGAFAIyf5rby7QylRc6JxU5lzQ9c4tN&index=41
'운영체제' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글
공지사항
최근에 올라온 글
최근에 달린 댓글
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
링크
TAG
- Flume
- Disk Scheduling
- JSON
- I/O Mechanisms
- vmware
- Disk System
- HDFS
- Replacement Strategies
- hadoop
- maven
- SQL
- aop
- Variable allocation
- Free space management
- Allocation methods
- File Protection
- Spring
- jdbc
- oracle
- I/O Services of OS
- springboot
- 빅데이터
- Java
- 하둡
- linux
- SPARK
- RAID Architecture
- 빅데이터 플랫폼
- gradle
- mapreduce
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
글 보관함
